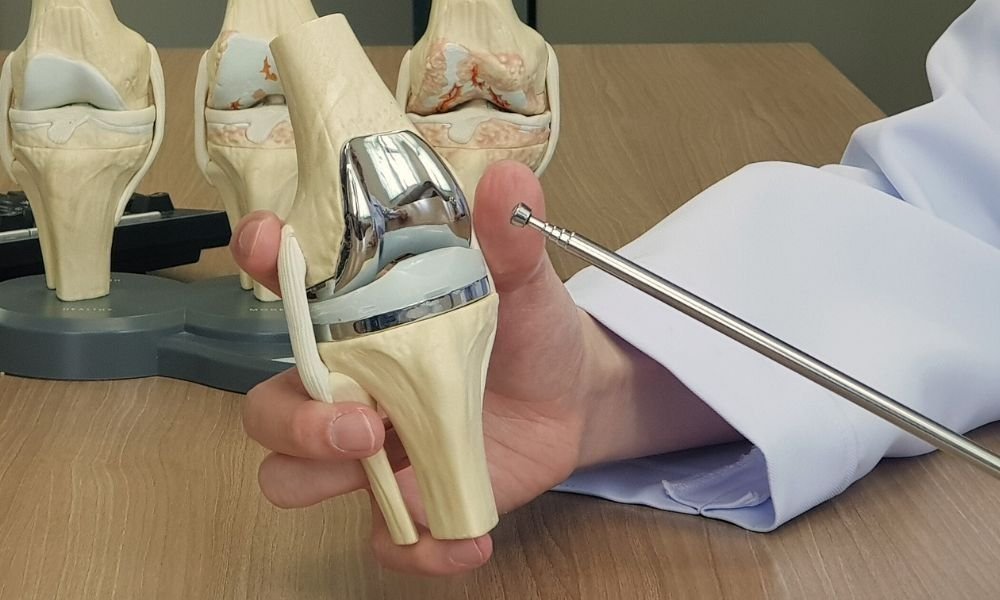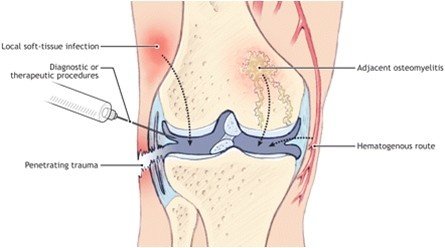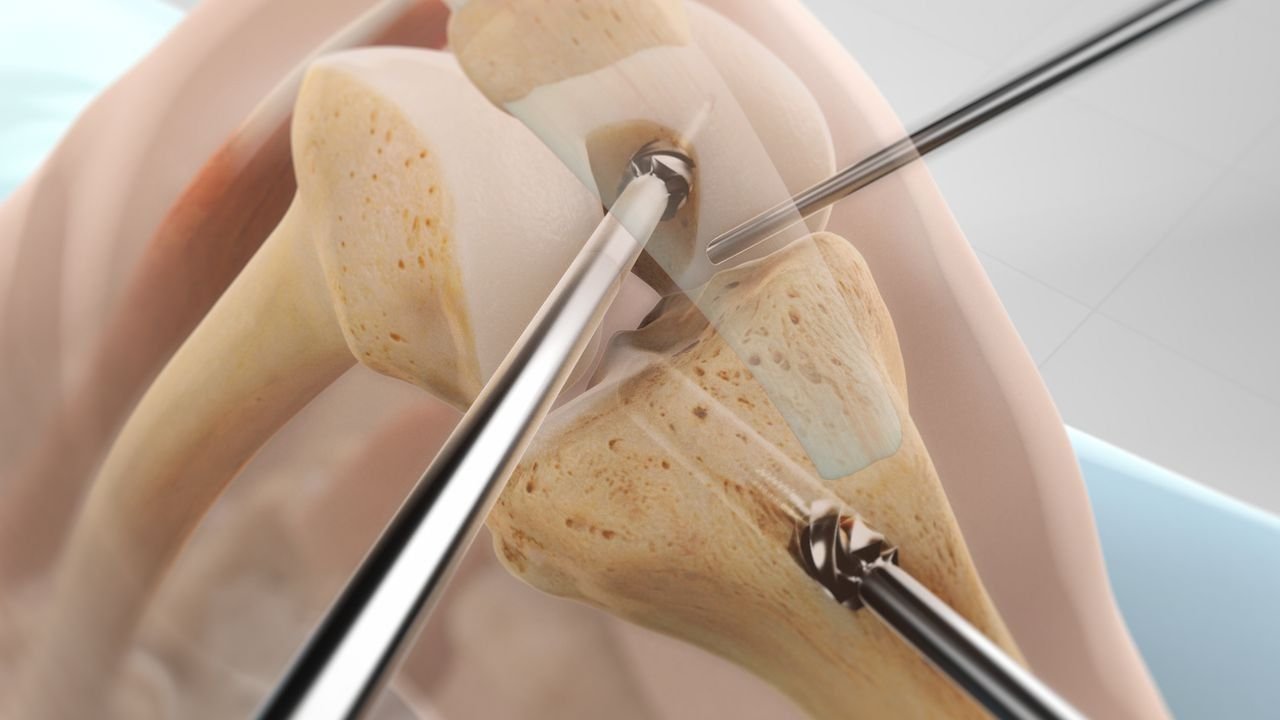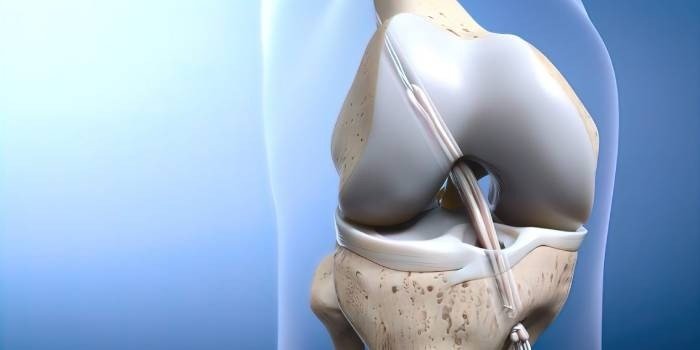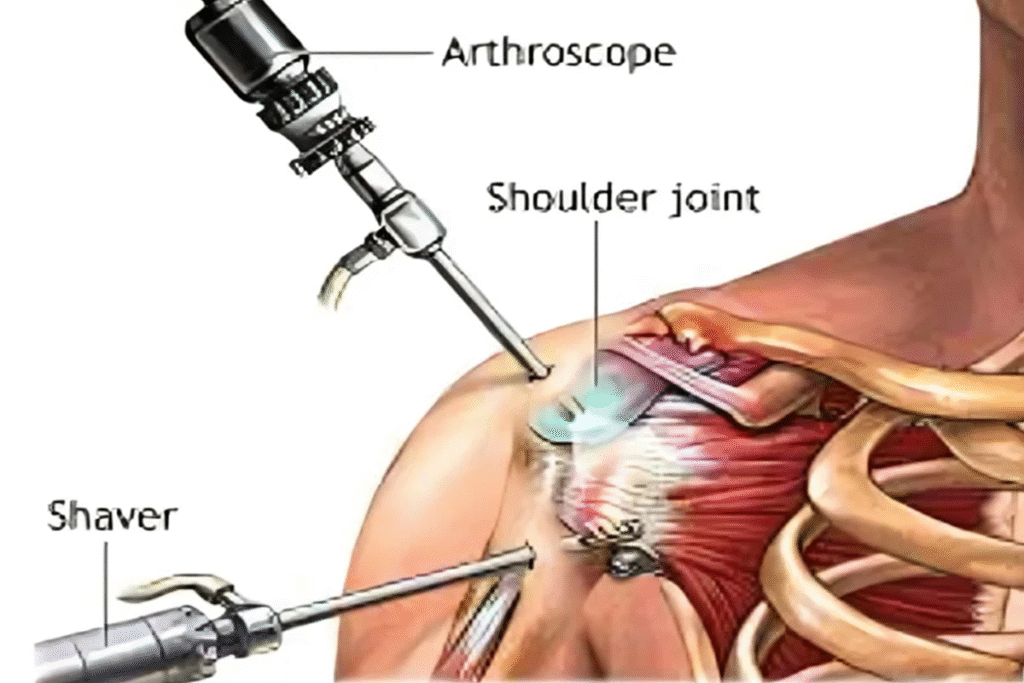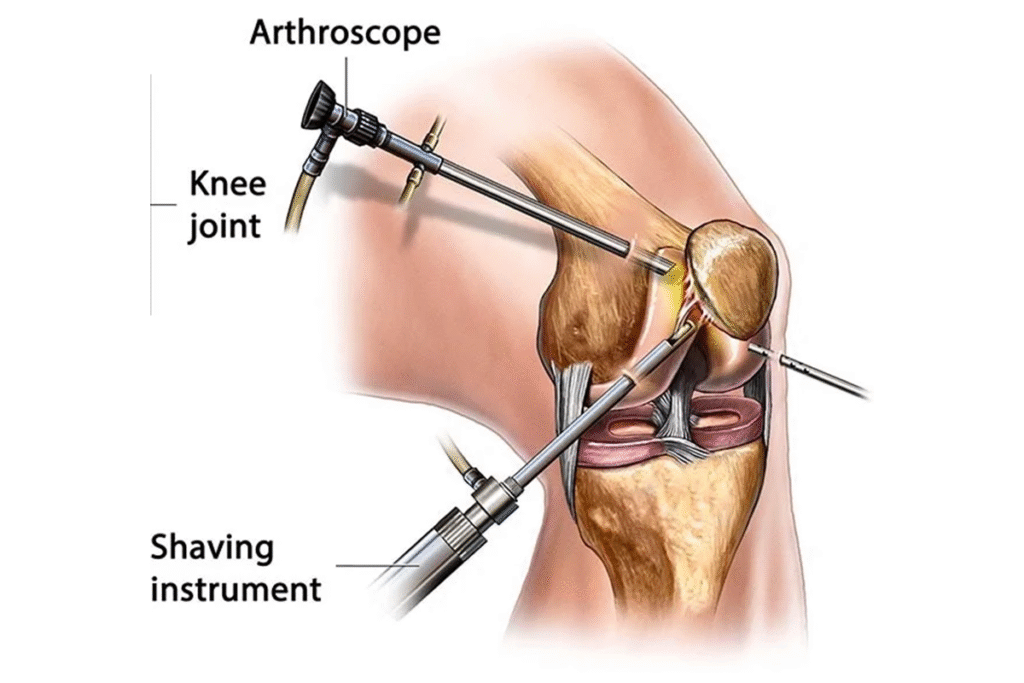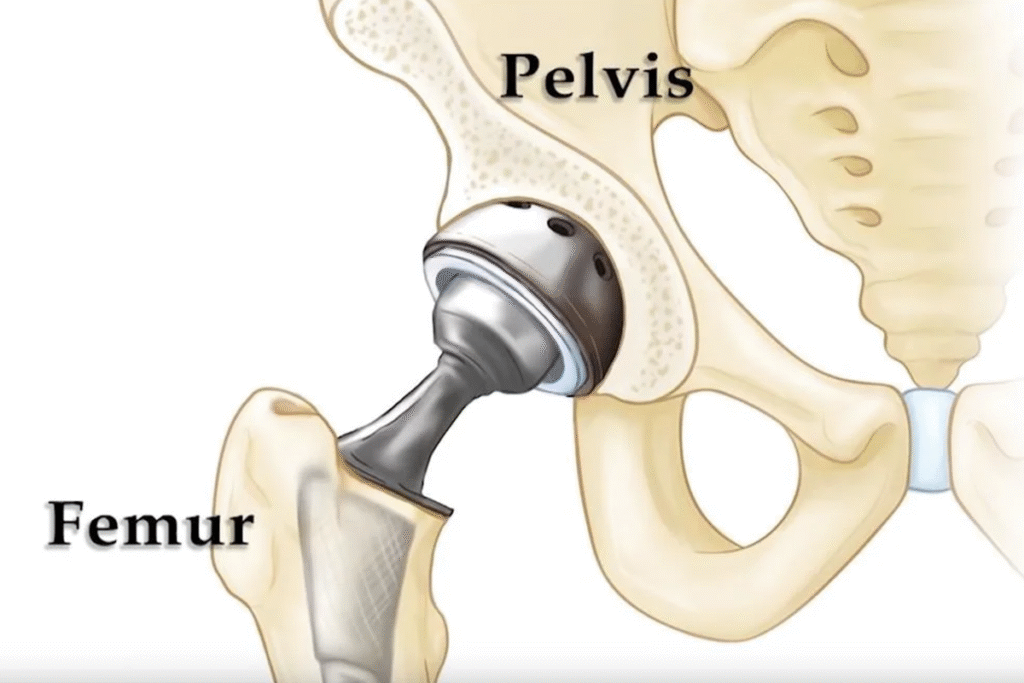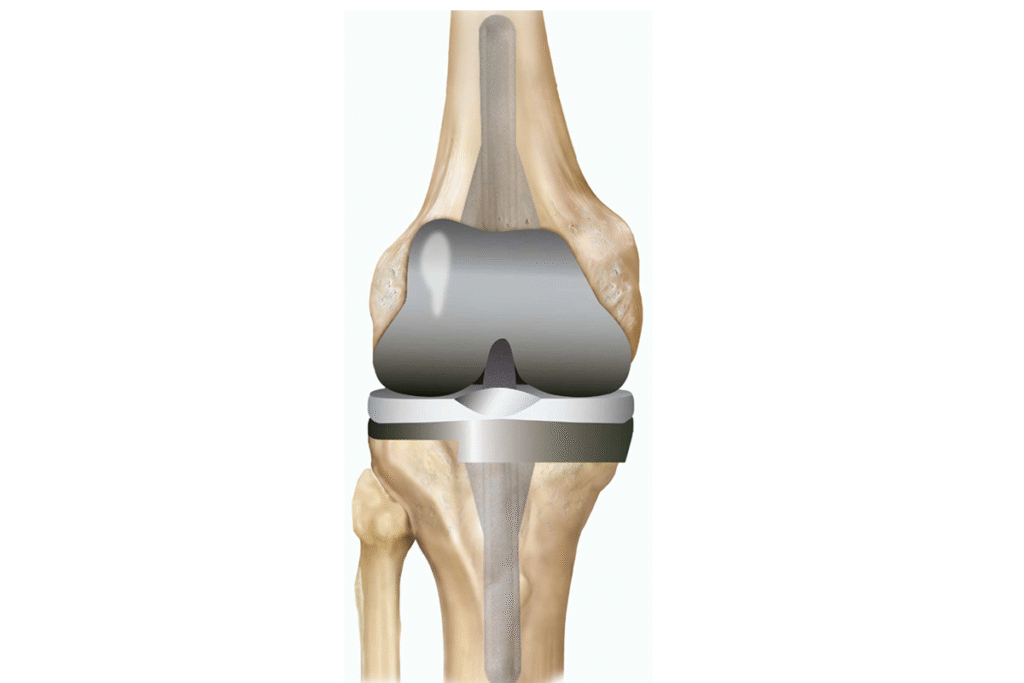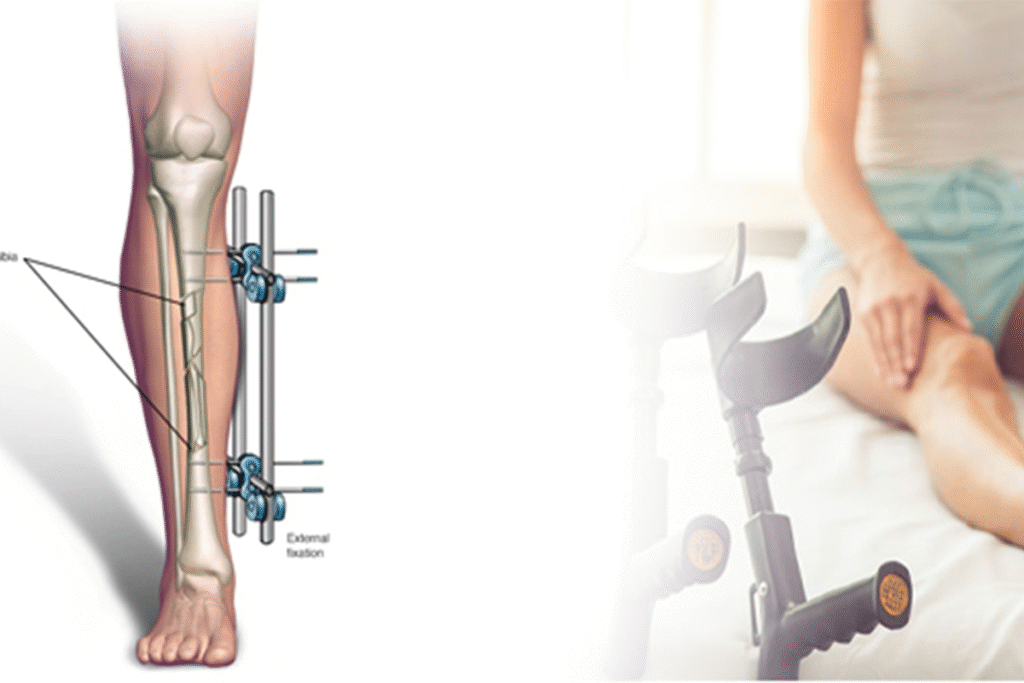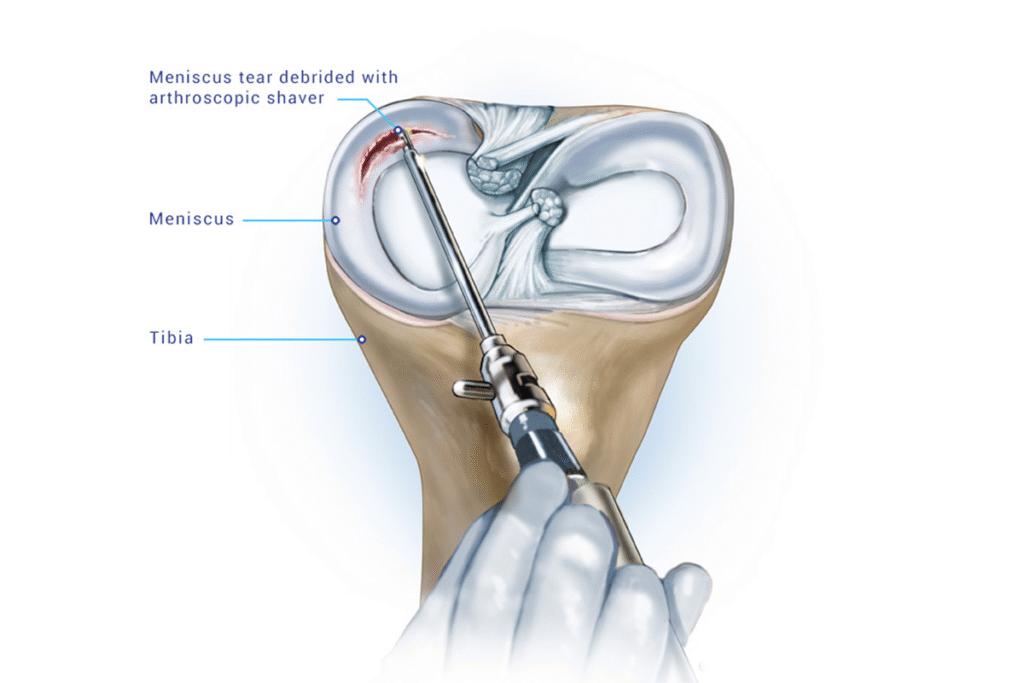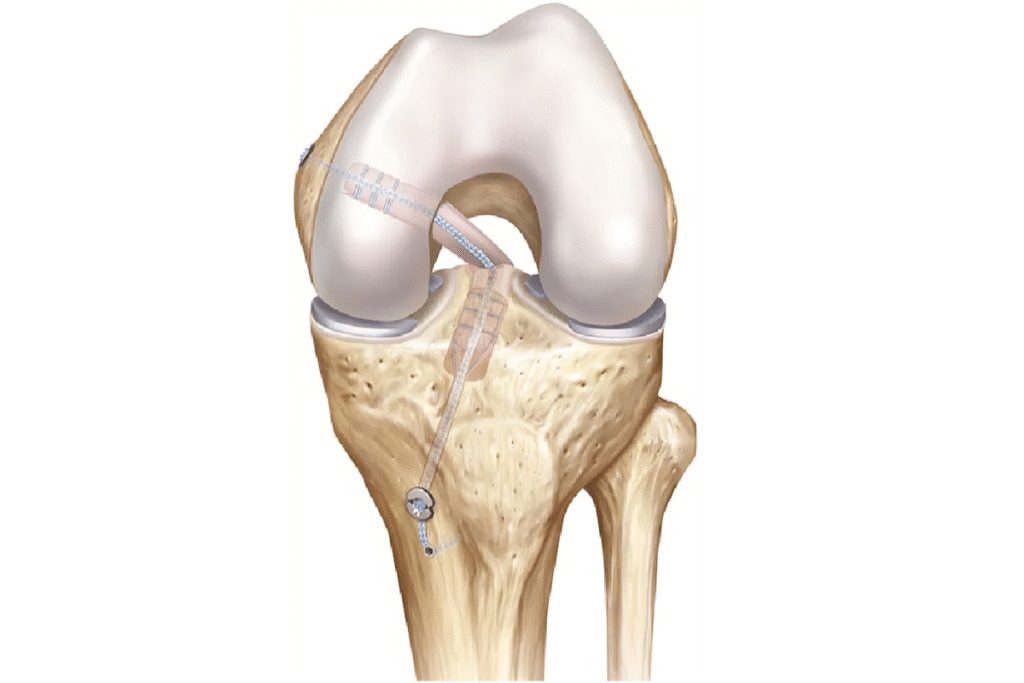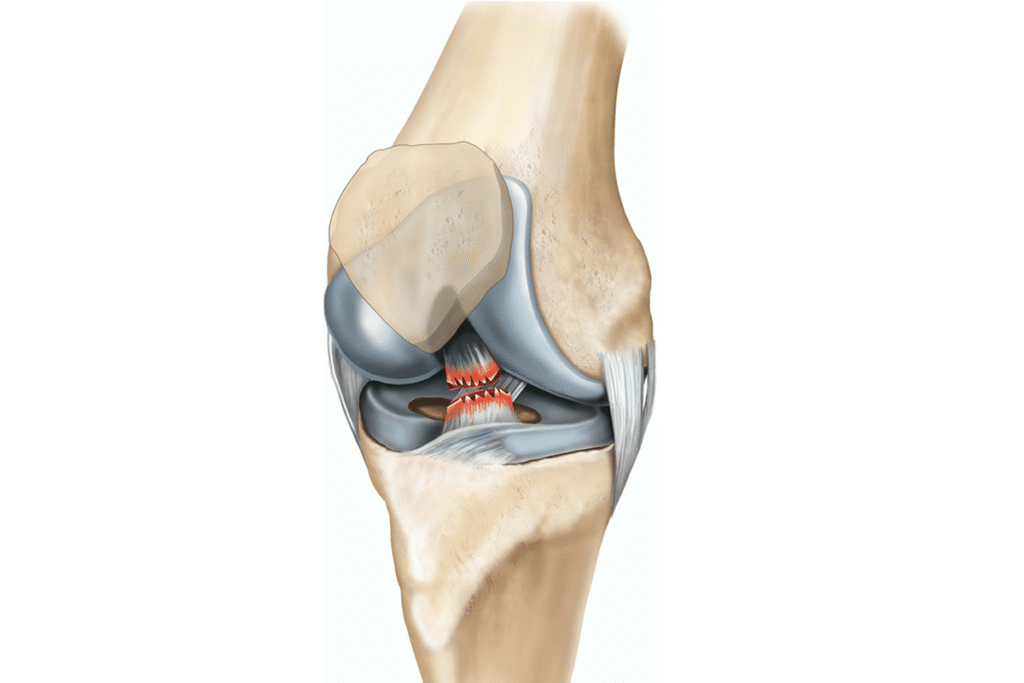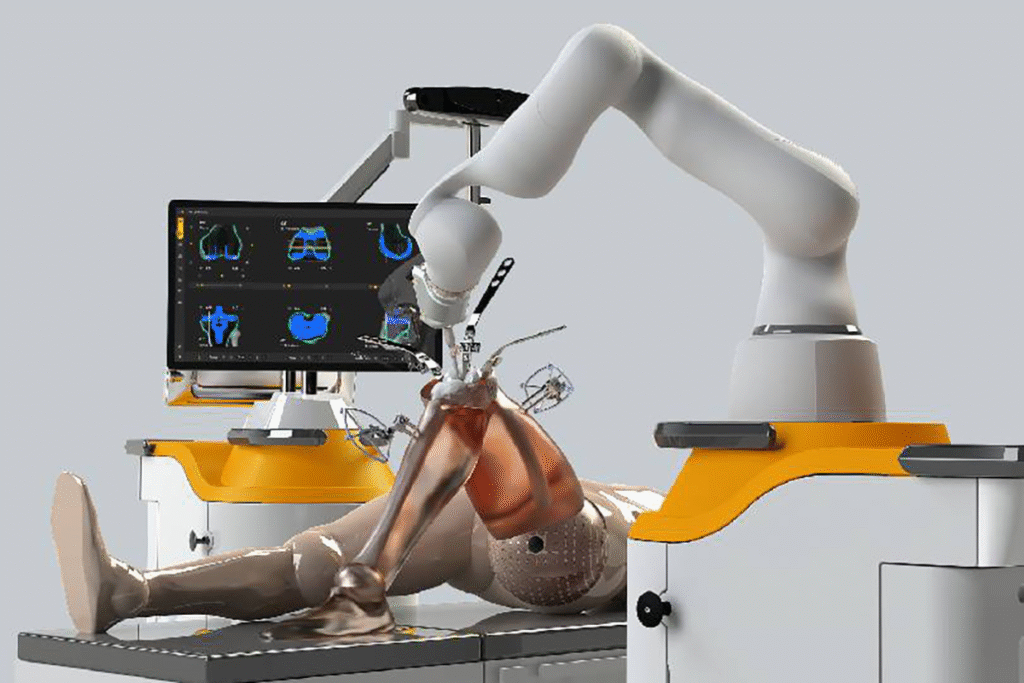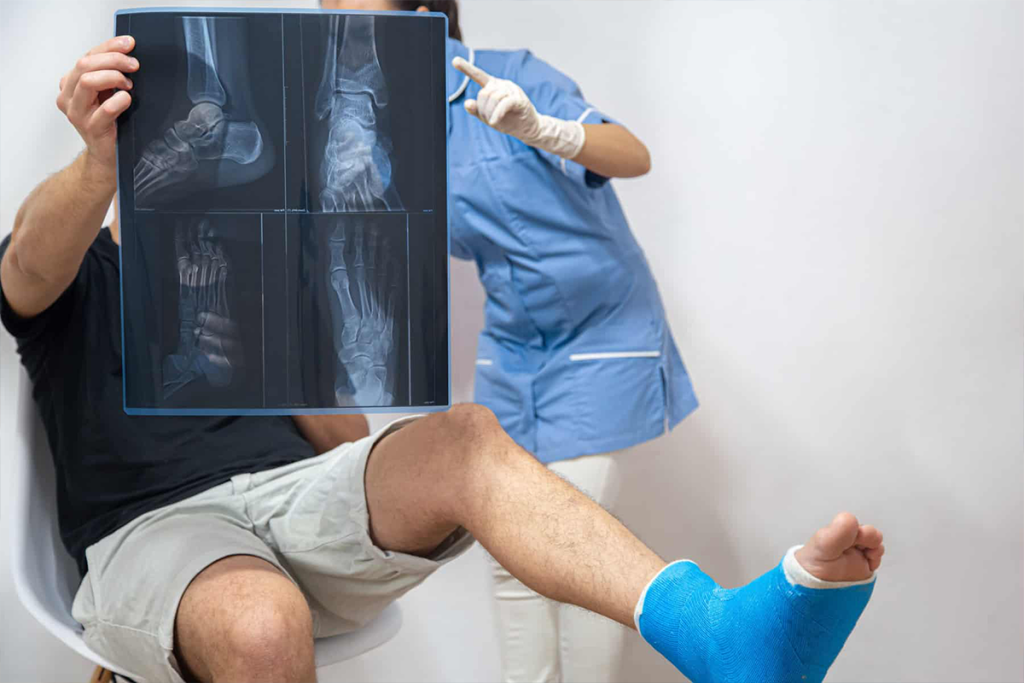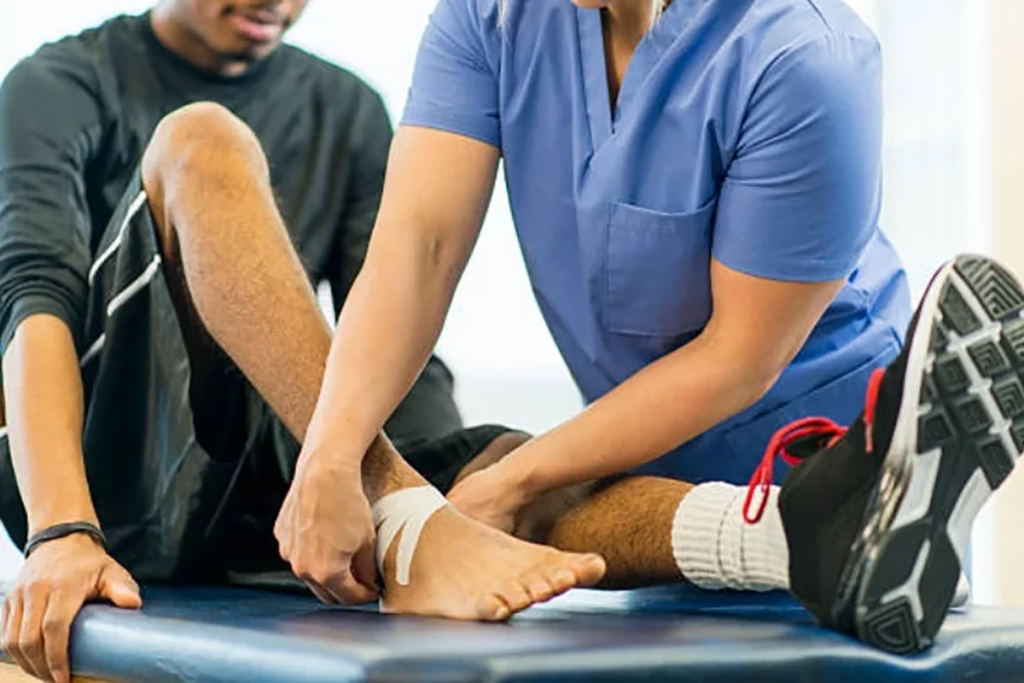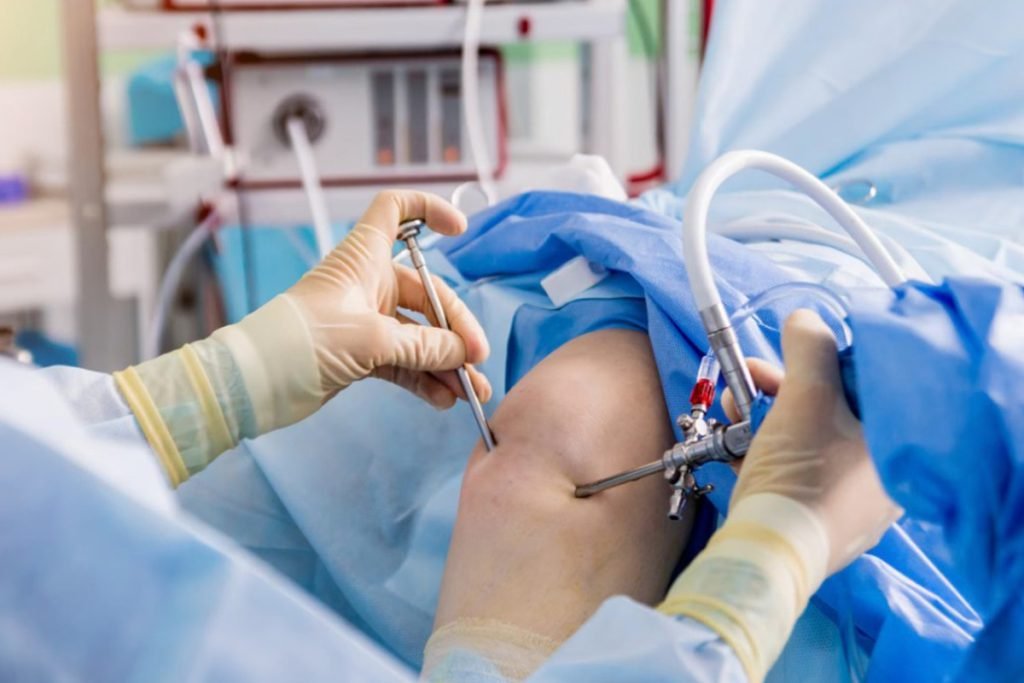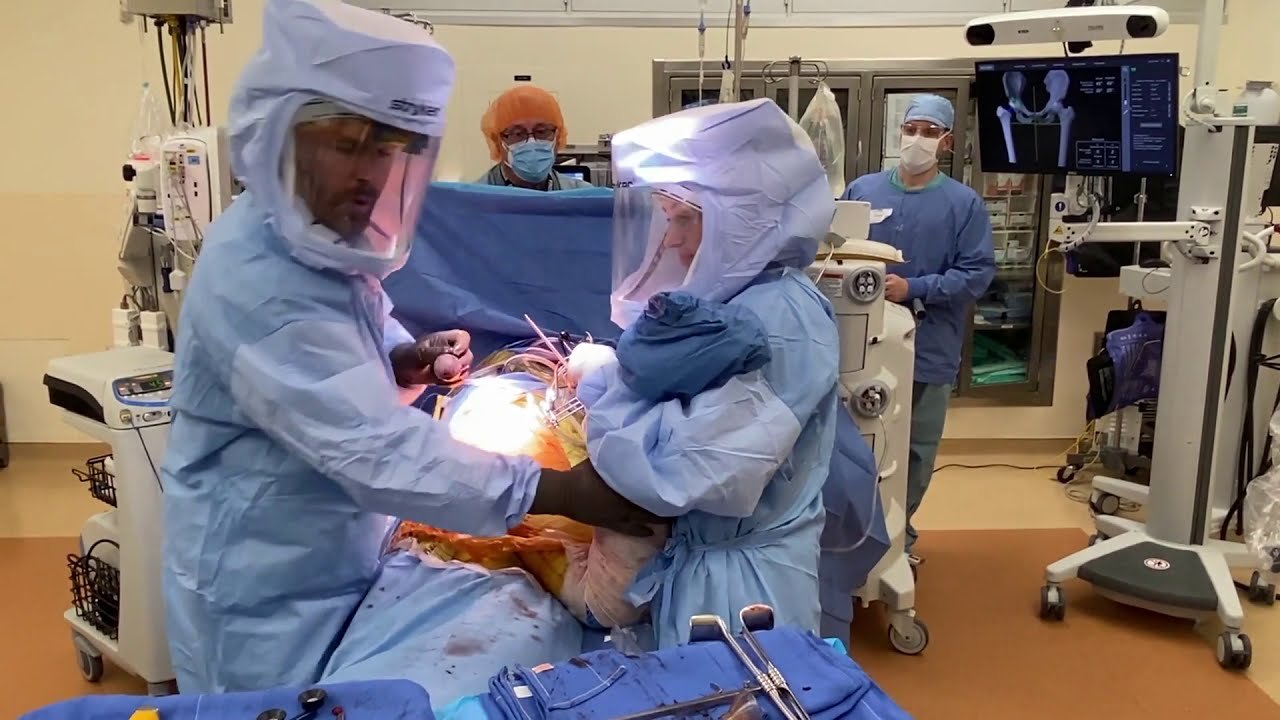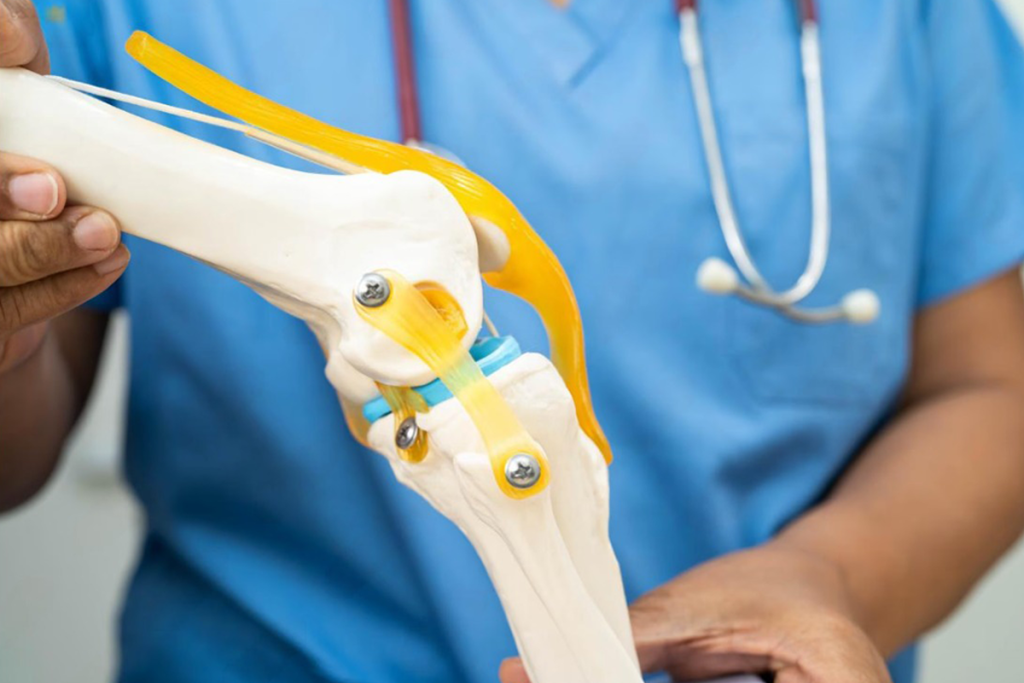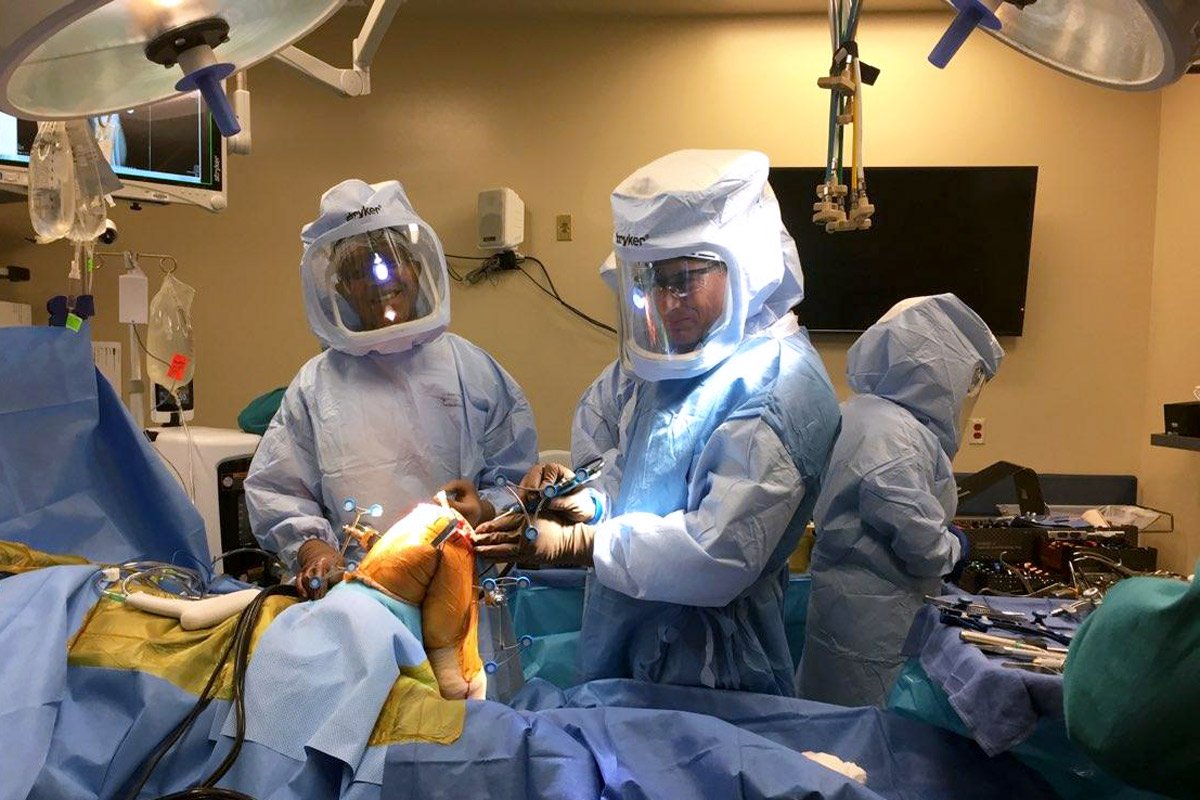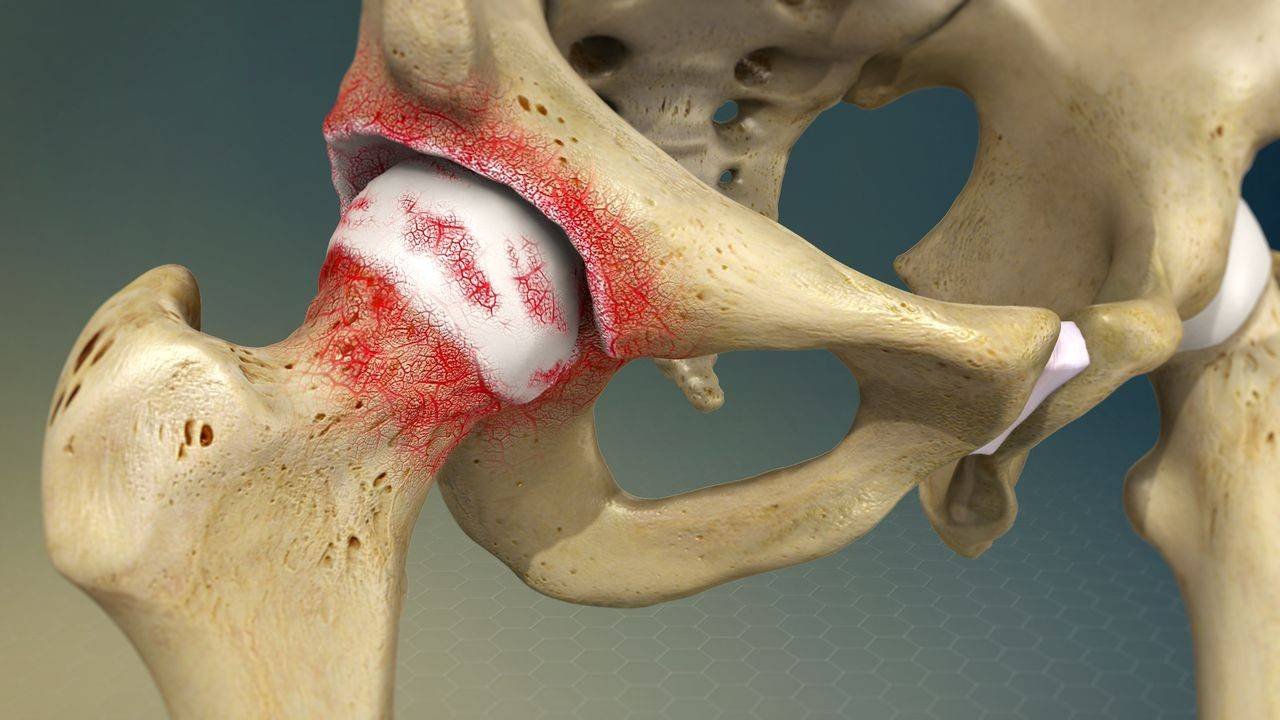
What advanced surgical techniques are used for the Best Hip Arthritis Treatment in Gurugram Sector 46?
Hip arthritis can severely affect mobility, comfort, and overall quality of life. Persistent hip pain, stiffness, and difficulty walking are common signs that require expert